|
Vitamin
|
Chemical Name
|
Deficiency Diseases
|
|
A
|
Retinol
|
Night blindness Xerophthalmia
|
|
B₁
|
Thymine ( Beri-Beri)
|
It is a skin & bone disorder disease.
|
|
B₂
|
Riboflavin
|
Cracking of skin, cracking of lips, & tongue.
|
|
B₃
|
Niacin or Nicotinamide (niacinamide)
|
Whitening of hair, Dementia (Loss of Memory), Insomnia
|
|
B₅
|
Pantothenic Acid
|
Pellagra of 4 D’s Syndrome (Diarrhoea, Diphtheria, Dementia, Death)
|
|
B₆
|
Pyridoxine
|
Skin disorders
|
|
B₇
|
Biotin
|
Hair fall, Dementia, Anemia
|
|
B₁₂
|
CyanoCobalamin
(Natural content of cobalt)
|
Anemia, Skin disorder, Insomnia
|
|
C
|
Ascorbic acid
|
Bleeding of Gums (Pyorrhea) Swelling of Gums.
|
|
D
Only vitamins not prepared in our body
|
Calciferol
|
1. Rickets → Child
2. Osteomalacia → Male
3. Osteoporosis → Female
|
|
E
|
Tocopherol
|
Less fertility
|
|
K
|
Phylloquinone
|
Non-clotting of blood
|
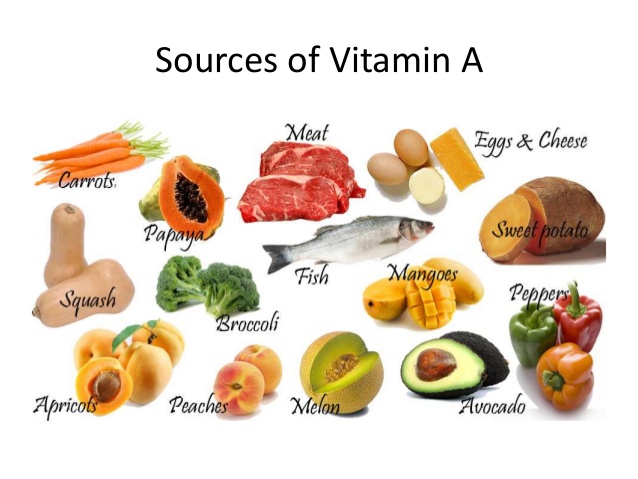
| Vitamin A | |
| Source | Dairy products, cod liver oil, liver, dark green and yellow vegetables and fruits |
| Function |
|
| SYMPTOMS OF DEFICIENCY |
|
| SYMPTOMS OF EXCESS |
|
| Vitamin B | |
| Source | Cow milk, sprouts, meat, eggs |
| Function |
|
| SYMPTOMS OF DEFICIENCY |
|
| SYMPTOMS OF EXCESS |
|
| Vitamin C | |
| Source | Citrus fruits(orange, grapefruit, lemon), strawberry, black currant, kiwi fruit, tomato, green leafy vegetables, green pepper |
| Function |
|
| SYMPTOMS OF DEFICIENCY |
|
| SYMPTOMS OF EXCESS |
|
| Vitamin D | |
| Source | Egg yolk, liver, cod liver oil, fish |
| Function |
|
| SYMPTOMS OF DEFICIENCY |
|
| SYMPTOMS OF EXCESS |
|
| Vitamin E | |
| Source | Green leafy vegetables, whole-wheat cereals, nuts, sprouts, egg yolk |
| Function |
|
| SYMPTOMS OF DEFICIENCY |
|
| SYMPTOMS OF EXCESS |
|
| Vitamin K | |
| Source | Green leafy vegetables, soya beans |
| Function |
|
| SYMPTOMS OF DEFICIENCY |
|
| SYMPTOMS OF EXCESS |
|
Q1. Beriberi is caused due to—
A. Vitamin A
B. Vitamin B
C. Vitamin C
D. Vitamin D
Ans-> Vitamin B
Q2. Vitamin D is also known as—
A. Reproductive vitamin
B. Sunshine vitamin
C. Ascorbic acid
D. Growth vitamin
Ans-> Sunshine vitamin
Q3. The vitamin which is water soluble?
A. Vitamin A
B. Vitamin B
C. Vitamin K
D. Vitamin D
Ans-> Vitamin B
Q4. A vitamin that plays a vital role in the coagulating property of blood?
A. Vitamin A
B. Vitamin B
C. Vitamin K
D. Vitamin D
Ans-> Vitamin K
Q5. Rickets is caused due to—
A. Vitamin A
B. Vitamin B
C. Vitamin C
D. Vitamin D
Ans-> Vitamin D
Q6. Vitamin D is—
A. Pyridoxin
B. Tocoferol
C. Ergosterol
D. Calciferol
Ans-> Calciferol
Q7. Scurvy is caused due to—
A. Vitamin B2
B. Ascorbic acid
C. Glutamic acid
D. Vitamin B12
Ans-> Ascorbic acid
Q8. Which of the following vitamin is responsible for remembering dreams?
A. Vitamin B
B. Vitamin B6
C. Vitamin A
D. Vitamin C
Ans-> Vitamin B6
Q9. Vitamin B6 is known as—
A. Pyridoxin
B. Tocopherol
C. Thiamine
D. Riboflavin
Ans-> Pyridoxin
Q10. Vitamin B12 contains—
A. Mn
B. Fe
C. Co
D. Mg
Ans-> Co




 Top 30 General Science Question for RRB ...
Top 30 General Science Question for RRB ...
 परमाणु संरचना का अध्ययन...
परमाणु संरचना का अध्ययन...
 जीव विज्ञान की विभिन्न शाखाएँ और उनका अध...
जीव विज्ञान की विभिन्न शाखाएँ और उनका अध...


