Theory Of Demand And Supply
The theory Of Demand And Supply is one of the most important theories in Economics or we can say one of the most important pillars of economics. It represents the relationship between buyers and sellers in a real market. In simple terms, when the price and supply of a commodity rise, the demand for that commodity falls and vice-versa. The level of supply and demand for varying prices of a commodity in an open market is represented on a graph known as the Demand and Supply Graph. The theory of demand and supply provides a framework for understanding market dynamics, price fluctuations, and the allocation of resources in a market economy. It helps economists, businesses, and policymakers analyze and predict market behavior and make informed decisions.
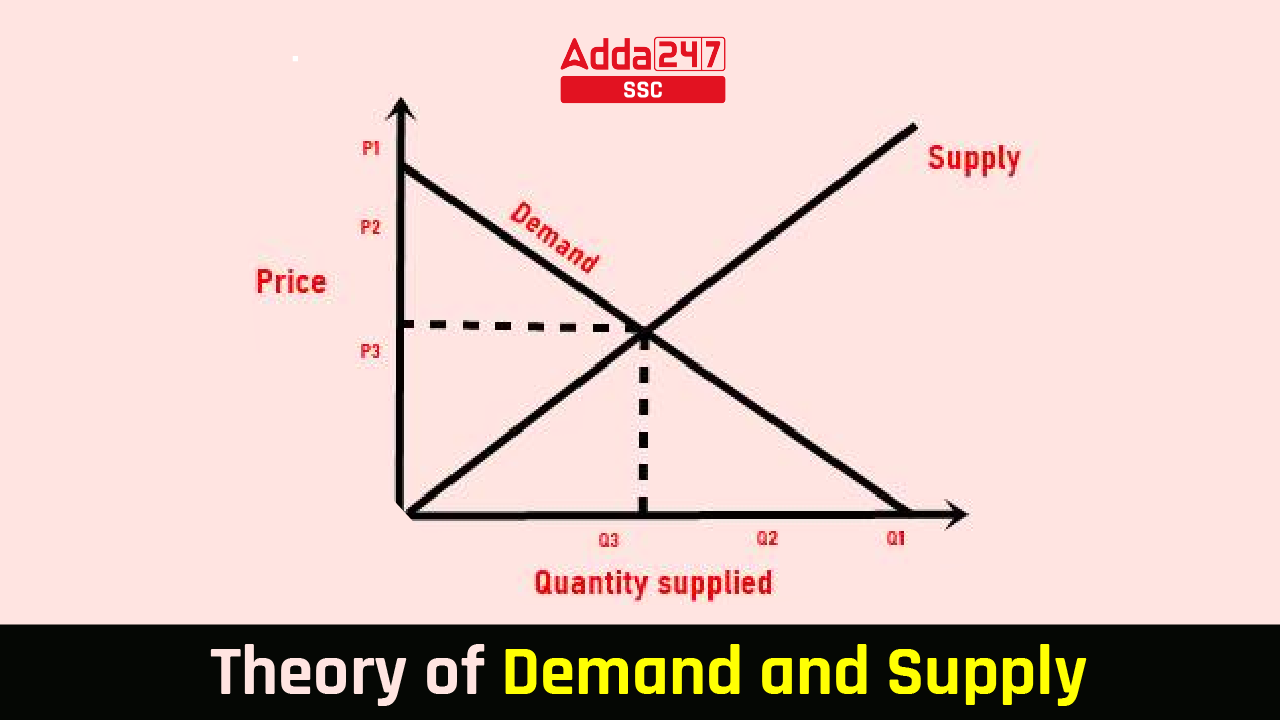
The relationship between demand and supply determines the market equilibrium.
Adam Smith, also known as the Father of Economics explained the concept of supply and demand as an “invisible hand” that naturally guides the economy. In this article, we will study in detail the Demand And Supply Theory.
Demand Theory
Demand is the customer’s desire to buy a commodity or service at a particular price during a given period of time. There are two aspects of demand- The consumer’s willingness to buy a particular product and the consumer’s ability to pay for the desired product.
Determinants of Demand
The determinants of demand or the factors influencing the demand of the consumers or buyers are as follows:
- Price of the commodity: The price of the commodity is inversely proportional to the demand for the commodity. If the price of the commodity increases then its demand will decrease and vice-versa.
- Income of the consumers: It means the capacity of the consumers to pay for a specific commodity. It is directly proportional to the demand for the commodity i.e. if the income of the consumers is high then the demand for various commodities will also be high.
- Consumer Preferences: This depends upon the season. For example, during summer the demand for air conditioners is very high and during winter the demand for air conditioners is very less.
Law of Demand
The Law of Demand states that if the price of a commodity is high then its demand will decrease and if the price of the commodity falls then its demand will increase.
We can understand this from the image shared below.
Supply Theory
Supply refers to the service or commodity provided to the consumers/buyers by the sellers at a particular price during a given period of time. Supply is correlated with demand and both together influence the market equilibrium.
Determinants of Supply
The determinants of supply are:
- Willingness: It is the quantity of the commodity sellers are willing to sell to the buyers/consumers
- Ability to sell/supply: The quantity of the commodity available to sell or supply to fulfill the demand of the consumer
Law of Supply
The law of supply states that when the price of a commodity increases then the quantity of supply or produce also increases and when the price of a commodity decreases the supply also decreases. The higher the price of the supply the higher will be the profit margin.
Demand And Supply Theory
Now, we will understand the relationship between demand, supply, and price listed below.
- Prices fall when supply increases and demand remains constant.
- Prices fall when demand decreases and supply remains constant
- Prices rise when supply decreases and demand remains constant
- Prices rise when supply decreases and demand remains constant
Check the difference between demand and supply from the table below.
| Particulars | Demand | Supply |
| Meaning | The desire of the consumer to buy the product | Supply refers to the service or commodity offered by the seller |
| Curve | Downward Slope | Upward Slope |
| Price Relationship | Inversely Proportional | Directly Proportional |
| Applicable to | Consumers | Sellers |
| Determinants | Price of the commodity
Income of the consumer Preference of the consumer |
The demand for the commodity
Willingness to sell Price of the commodity Competitors available in the market |
Equilibrium Point
The equilibrium point, also known as market clearing price or market equilibrium is a situation where the demand of the commodity and supply of the commodity intersects. At this point, both the buyers and sellers are satisfied and this represents the market equilibrium. Market equilibrium helps the business to stabilize and survive in the market for a longer course of time. Disequilibrium, which is when there is a difference in the demand and supply of the commodity affects the markets, the business entity, and the economy of the country.
| Check Other Links: | |
| National Language of India | Basics of Accounting Principles |
| Prime Ministers of India | List of Presidents of India |


 How can I get selected for Delhi Police ...
How can I get selected for Delhi Police ...
 SSC CHSL Vs. SSC CGL – What Changes in S...
SSC CHSL Vs. SSC CGL – What Changes in S...
 Importance of Solving Previous Year Pape...
Importance of Solving Previous Year Pape...










