Table of Contents
National Language of India
National Language of India: India that is “Bharat” is known for its vast and rich culture and is composed of 28 states and 8 Union Territories. All the states and union territories have their own unique heritage, dialect, and language. It is said that India is the only country where language changes in every 100 kms of areas, and that is why India has no national language. Indian English and Modern Standard Hindi are the official languages of India. It is to be noted that national language and official language both are different things. There were only 14 languages at the time of commencement of the Indian constitution. The eighth schedule of the constitution of India says that there are 22 languages that are spoken in Indian states. For more information about the national languages of India, read the below article till the end.
Which is the National Language of India?
India doesn’t give the status of the National language to any of the languages due to the diversity of the country. Hindi is a language spoken by less than 44% of people in India. The debate to make Hindi an official language has sparked for decades but to no avail. The Indian constitution does not give rights to any language to be declared as the National language of India. However, Hindi and English have been declared as the official languages to be used for official purposes throughout the country.
Official Language of India
Article 343(1) of the Indian constitution mentions that “The official language of the Union shall be Hindi in Devanagari script. The form of numerals to be used for the official purposes of the Union shall be the international form of Indian numerals.”
The business in the Indian parliament or the offices of government can only be transacted in Hindi or English. English is allowed to be used for official purposes throughout the country such as parliamentary proceedings, communications between the Central Government and a State Government, and judicial matters.
- Hindi is the language used by the Central Government as per Article 343 when communicating with the states of the Hindi Belt.
- English is the Associate official language and the language to be used while communicating with the states.
What is the difference between National and Official languages?
The National Language is any language that is spoken by a large proportion of the inhabitants of a nation. It is used for political, cultural, and social functions.
The official language is the language that is used for government matters, like in the national court, parliament, or business purposes, typically recognized and adopted by the government or in the legislature.
Hindi language would be used by the Central Government as per Article 343 when communicating with the Hindi states.
English is the Associate official language and the language to be used while communicating with the states.
So as per the Constitution of India, Hindi and English are the official languages and not the National languages.
List of 22 languages of India
22 languages have been recognized in the eighth schedule of the Indian constitution. Part XVII of the Indian constitution deals with the official languages of India from articles 343 to 351. Originally, only 14 languages were mentioned and later, after several amendments, the other languages were added. Check out the list of all the 22 languages of India as recognized by the Indian constitution.
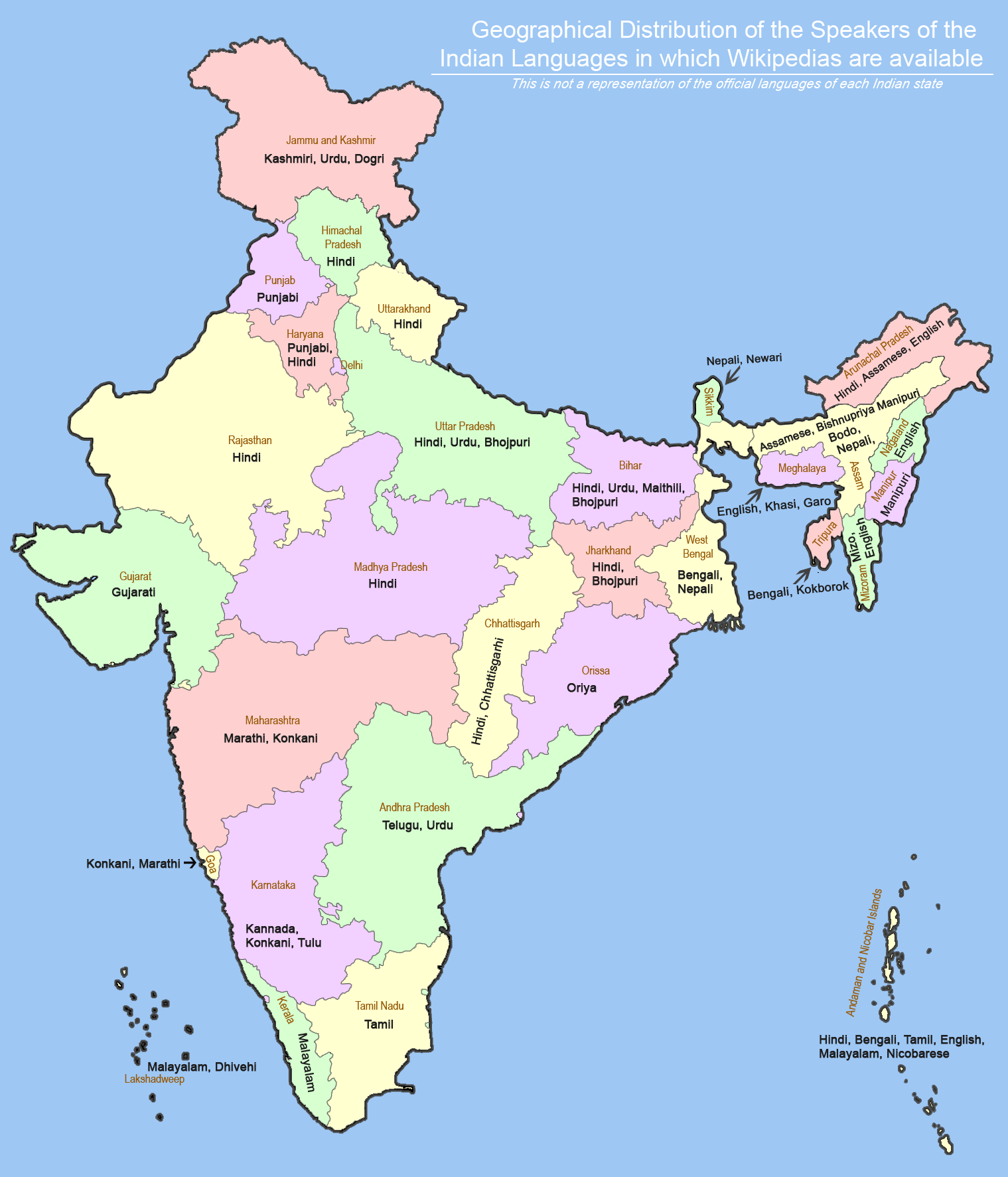
| Sr. No | Language | Recognition in state |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Assamese | Assam, Arunachal Pradesh |
| 2 | Bengali | West Bengal, Tripura |
| 3 | Bodo | Assam |
| 4 | Dogri | The official language of Jammu and Kashmir |
| 5 | Gujarati | Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu, Gujarat |
| 6 | Hindi | Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Bihar, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu, Chhattisgarh, Delhi, Gujarat, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Mizoram, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and West Bengal |
| 7 | Kannada | Karnataka |
| Kashmiri | Jammu and Kashmir | |
| 9 | Konkani | Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu, Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, and Kerala (The Konkan Coast) |
| 10 | Maithili | Bihar, Jharkhand |
| 11 | Malayalam | Kerala, Lakshadweep, Puducherry |
| 12 | Manipuri | Manipur |
| 13 | Marathi | Maharashtra, Goa, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu |
| 14 | Nepali | Sikkim and West Bengal |
| 15 | Odia | The official language of Orissa |
| 16 | Punjabi | The official language of Punjab and Chandigarh, 2nd official language of Delhi and Haryana |
| 17 | Sanskrit | Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand |
| 18 | Santali | Spoken by Santhal people mainly in the state of Jharkhand as well as in the states of Assam, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Mizoram, Odisha, Tripura, West Bengal |
| 19 | Sindhi | Gujarat and Maharashtra, especially Ulhasnagar |
| 20 | Tamil | Tamil Nadu, Puducherry |
| 21 | Telugu | Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Puducherry |
| 22 | Urdu | Jammu and Kashmir, Telangana, Jharkhand, Delhi, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and West Bengal |
| Other Related Links: | |
| Largest State in India | PM Kisan Beneficiary List |
| List of Prime Ministers of India | Union Territories of India |
| National Symbols of India | President Salary in India |




 States and Capitals in India, List of 28...
States and Capitals in India, List of 28...
 List of Presidents of India from 1950 to...
List of Presidents of India from 1950 to...
 List of Neighbouring Countries of India ...
List of Neighbouring Countries of India ...


