Table of Contents
Candidates preparing for the Railway Recruitment Board NTPC understand the significance of the Geometry section. This topic is an important part of the mathematics section in both stages of the CBT conducted in the NTPC exam. With proper preparation, candidates can easily tackle 3-4 geometry questions in the exam.
To help you score full marks in this section, we have compiled a set of 20 important Geometry questions with detailed solutions. These practice questions will give you an idea of the types of questions asked in the RRB NTPC 2025 exam and also help you assess your current preparation level.
Geometry Questions for RRB NTPC
Geometry is an important part of the RRB NTPC Syllabus 2025, covering various 2D and 3D shapes that frequently appear in the exam. Candidates are expected to solve questions related to angles, triangles, circles, quadrilaterals, and coordinate geometry. Mastering this section is important for improving accuracy and securing good marks. To help candidates practice effectively, we have provided a set of RRB NTPC Geometry Questions with detailed solutions below.
Q1. In ∆ABC, angle BAC = 90°. If BC = 30 cm, then what is the length of the median AD?
(a) 20 cm
(b) 15 cm
(c) 18 cm
(d) 19 cm
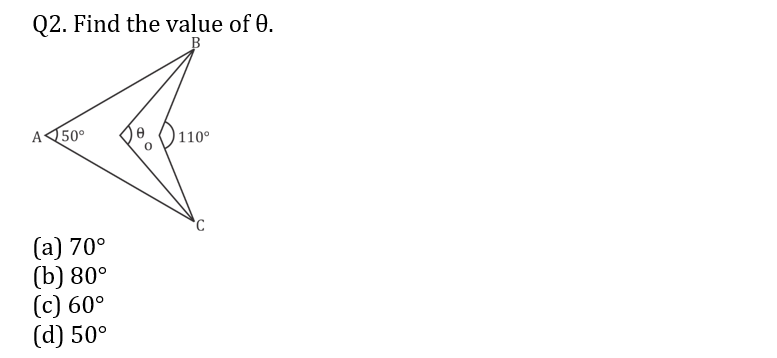
Q3. How many isosceles ∆ with integer sides are possible in which the sum of two sides is 14 cm?
(a) 25
(b) 24
(c) 21
(d) 22

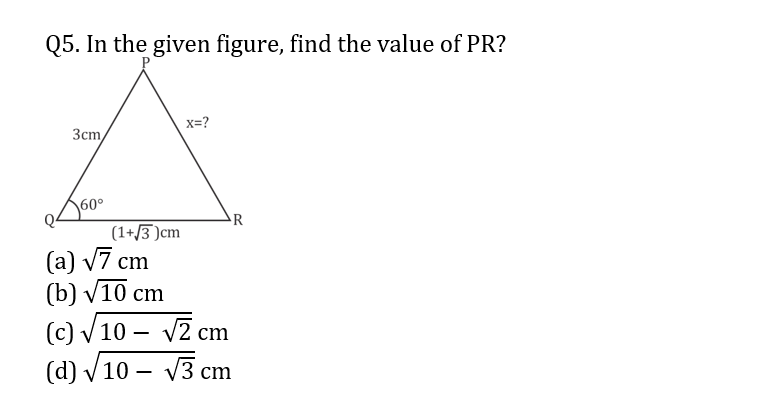
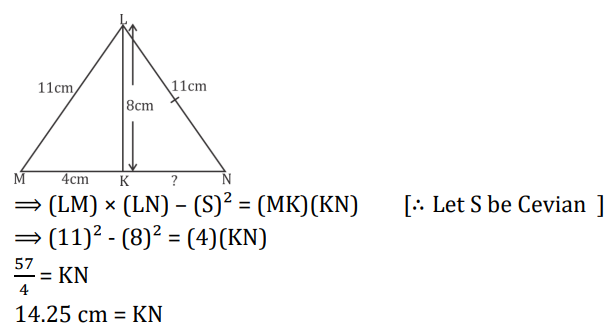
Q6. In ∆LMN, LM = LN, and K is a point on MN, if MK = 4 cm, LM = 11 cm, and LK = 8 cm, then the length of NK is?
(a) 14.25 cm
(b) 16 cm
(c) 18 cm
(d) 12 cm
Q7. The measure of sides (x² – 1), (x² + 1) and 2x cm. Then find the triangle is :
(a) Obtuse triangle
(b) Right angle triangle
(c) Isosceles triangle
(d) Scalene triangle
Q8. The inradius of a triangle is 12 cm and the sum of the length of its side is 100 cm. Find the area of the triangle.
(a) 500 cm²
(b) 300 cm²
(c) 400 cm²
(d) 600 cm2


Q11. A circle is inscribed in a triangle ABC. It touches sides AB, BC, and AC at points R, P, and Q, respectively. It AQ 7 cm, PC 6 cm, and BR 8 cm, then the perimeter of the triangle is:
(a) 42cm
(b) 50cm
(c) 25cm
(d) 45cm
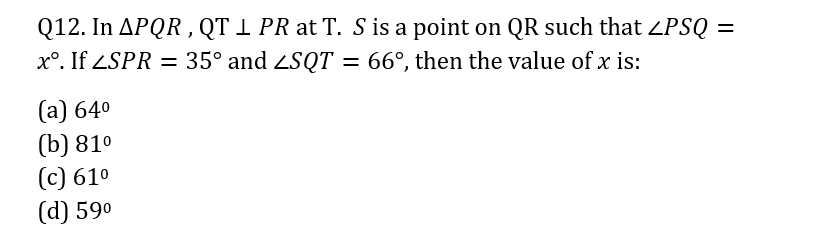
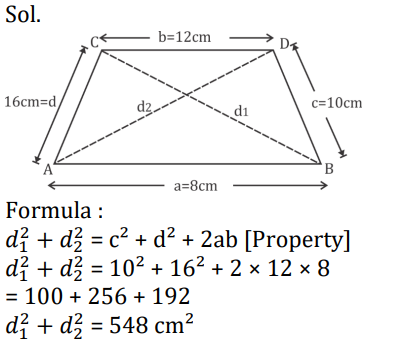
Q13. ABDC is a trapezium in which AB||DC and AB = 8cm, BD = 10cm, CD = 12cm, AC = 16cm, then AD² + BC² is equal to.
(a) 530 cm²
(b) 548 cm²
(c) 624 cm²
(d) 630 cm²
Q14. Number of sides of two regular polygons are in the ratio 3 : 4 and each of their interior angle are in the ratio 8 : 9. The number of sides of the two polygons are .
(a) 8, 12
(b) 4, 8
(c) 6, 15
(d) 6, 8
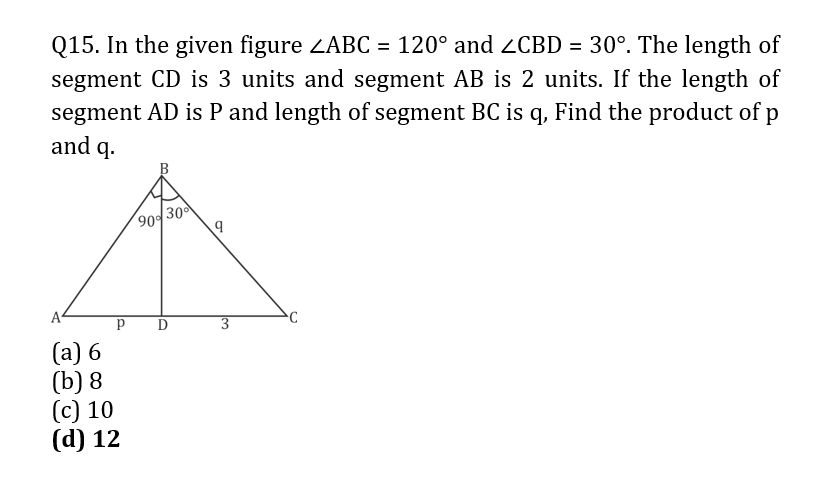

Q17. In ∆PQR, = 90°, PQ = 24 cm and PR = 18 cm. S is the mid-point of PR and ST at T. What is the area of ∆RST?
(a) 18.35cm2
(b) 17.25cm2
(c) 19.44cm2
(d) 15.67cm2
Q18. O is the incentre of ∆PQR. If ∠QOR = 108°, then ∠P = ?
(a) 380
(b) 560
(c) 450
(d) 360

Q20. AB is a chord in a circle with center O. AB is produced to C such that BC is equal to the radius of the circle. C is joined to O and produced to meet the circle at D. if ACD = 40°, then the measure of AOD is-
(a) 130°
(b) 125°
(c) 138°
(d) 120°
Geometry Questions for RRB NTPC with Solution PDF
Provided below is a solution PDF to go through for a better understanding of students. By going through the solutions, students can strengthen their knowledge and boost confidence. Candidates must refer to the below RRB NTPC Geometry Questions Solutions PDF.
S1. Ans.(a)
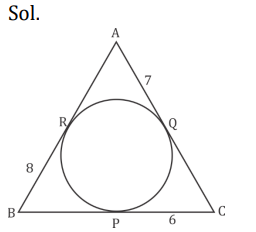
AQ = AR = 7cm (Tangents from the same external point to the circle)
BR = BP = 8cm (Tangents from the same external point to the circle)
and
PC and QC = 6cm (Tangents from the same external point to the
circle)
The perimeter of triangle ABC
2(AQ + PC + BR) = 2(7 + 6 + 8) = 42cm
S2. Ans.(d)
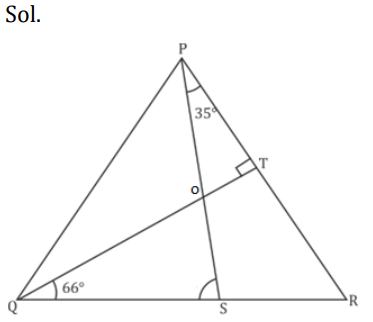
In ∆POT
∠POT + ∠OTP + ∠TPO = 180
∠POT = 55°
∠POT and ∠SOQ = 55°
In ∆QOS
∠QOS + ∠OSQ + ∠SQO = 180
55° + x° + 66 = 180°
x = 59°
S3. Ans.(b)
S4. Ans.(d)
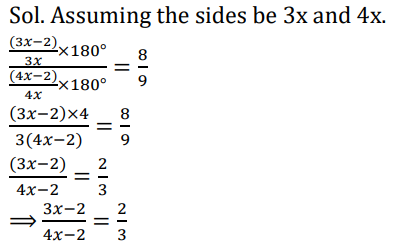
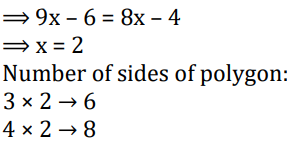
S5. Ans.(d)
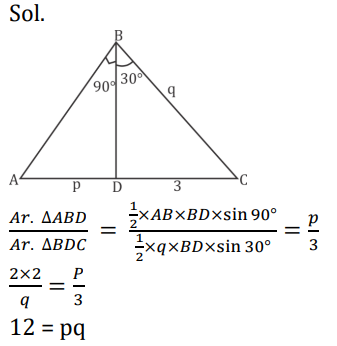
S6. Ans.(c)
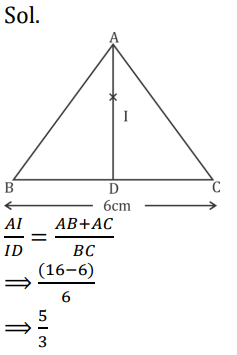
S7. Ans.(c)
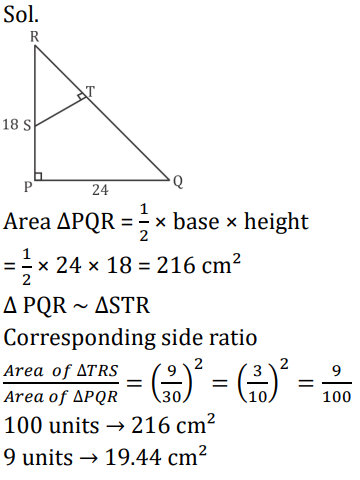
S8. Ans.(d)
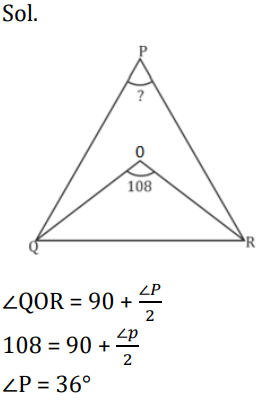
S9. Ans.(c)
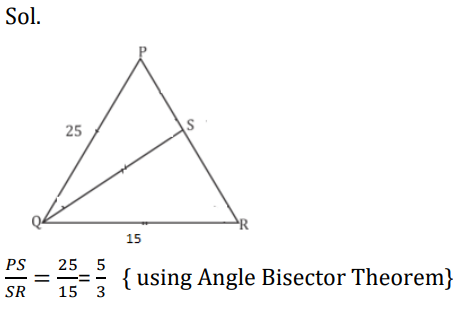
S10. Ans.(d)
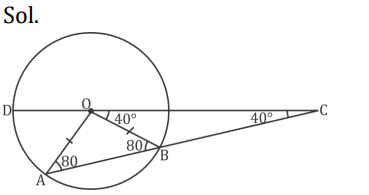
AO = BC (Given)
OA = OB (Radius circle)
∠AOD is exterior angle of ∆AOC
∠AOC = 80 + 40 = 120°
S11. Ans.(b)
Sol.
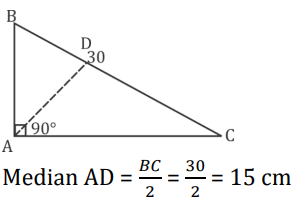
S12. Ans.(b)
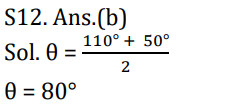
S13. Ans.(c)
Sol. Let the side of the triangle be x, x and y.
Case 1: (x + x = 2x =14 ) When both the sides are equal whose Sum is
given
|x – x|< Side < |x + x|
0 < a < 14
⟹ 13 triangles possible here.
Case 2: (x + y = 14) When both the sides are different
|x – x|< y < |x + x|
|x – x|< y < |2x|
|x – x|< y < |2 (14 – y)|
0 < y < |28-2y|
0 < 3y < |28|
0 < y < 9.33
Y can take value from 1 to 9 except 7, so, here y can take 8 value
13 + 8 = 21 triangles
S14. Ans.(a)
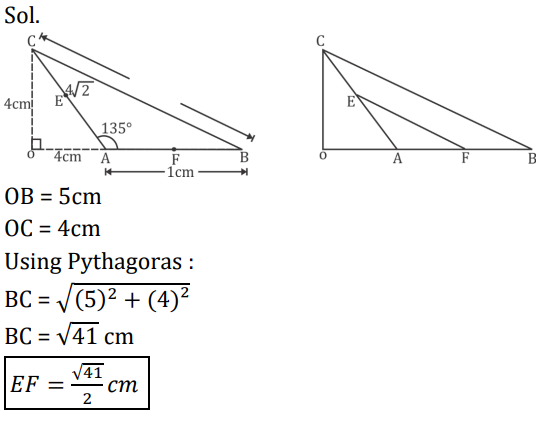
S15. Ans.(d)
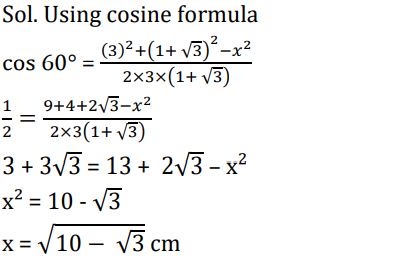
S16. Ans.(a)
Sol. Using Stewart theorem (Simplified Form)
S17. Ans.(b)
Sol. From options
Apply Pythagoras theorem
(x² + 1)² = (x² – 1)² + (2x)²
⟹ (x² + 1)² – (x² – 1) = (2x)²
⟹ x
4 + 1 + 2×2 – x
4 – 1 + 2×2 = 4×2
⟹ 4×2 = 4×2
Hence, it is a right-angle triangle.
S18. Ans.(d)
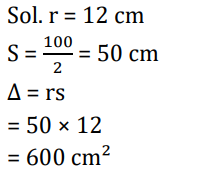
S19. Ans.(a)
Sol.
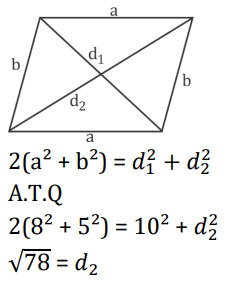
S20. Ans.(c)
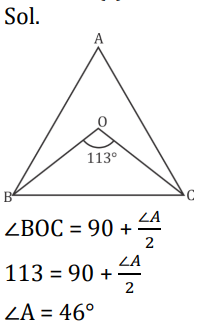








 RRB NTPC Salary 2025, Check Salary Struc...
RRB NTPC Salary 2025, Check Salary Struc...
 What are RRB NTPC Level 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 po...
What are RRB NTPC Level 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 po...
 RRB NTPC Exam Date 2025 for CBT 1 and CB...
RRB NTPC Exam Date 2025 for CBT 1 and CB...


