Table of Contents
Electrolysis is the process of breakdown of Electrolyte due to incorporation of Electric Current into it. The Electrolyte breaks itself into its ionic form and produces Cation and Anion through a non-spontaneous Chemical Reaction involving Oxidation and Reduction. It has huge applications in the Electroplating, Synthesis of various compounds, Refining of Ores and minerals (Eg.: Aluminum from Bauxite), and various analytical techniques (Eg.: Polarography Technique).
Electrolysis of Water
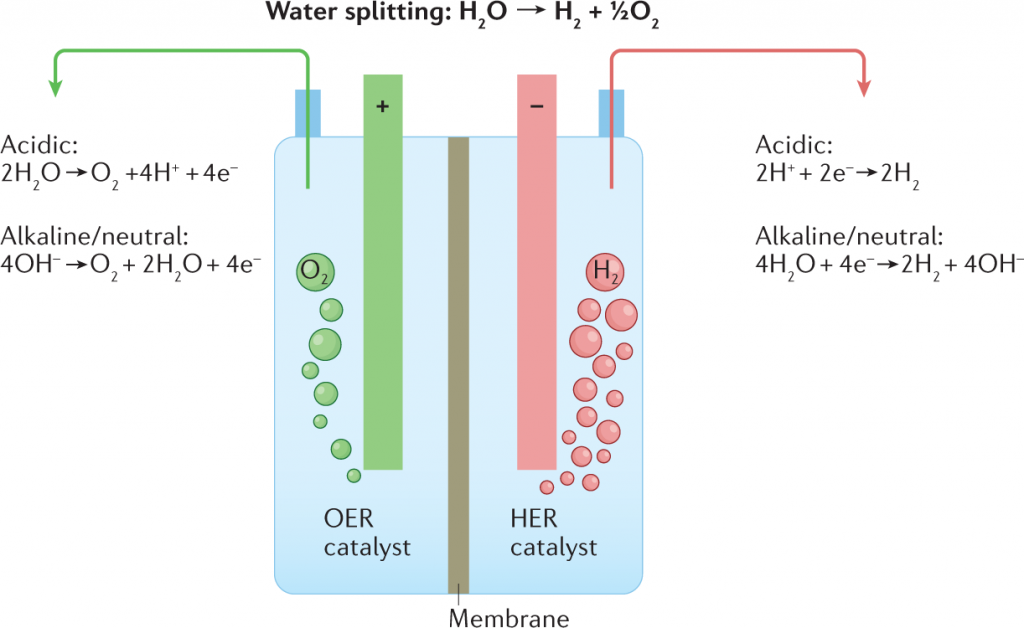
Electrolysis of water is the process of converting water (H₂O) into hydrogen (H+) and hydroxide (OH¯) ions by passing an electric current through it. Ions move to the opposing electrodes, releasing pure hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂) gases. Electrolysis of water is an oxidation-reduction reaction that does not occur spontaneously. Since the heat in the form of electricity is supplied to the electrolytic cell in the electrolysis of water, the reaction is endothermic. The process of Electrolysis of Water is also called “Water Splitting“.
Principle of Electrolysis of Water
The Principle for Electrolysis of Water is based on Decomposition due to Redox Reaction. In which, the Electrolyte loses and gains electrons simultaneously. The Oxidation can be seen at the Anode (positive terminal of Cell) while Reduction can be seen at Cathode (negative terminal of Cell), where electrons are lost and gained respectively.
The electrolysis of water is a decomposition reaction. This is because water splits into its constituent elements, hydrogen, and oxygen, under the effect of an electric current. The mole ratio of hydrogen and oxygen gases liberated during the electrolysis of water is 2:1. Since the Decomposition of Water at standard Temperature and Pressure is not possible thermodynamically, adding Catalyst such as Sulfuric Acid helps in the proceeding of the reaction.
Electrolysis of Water Methodology

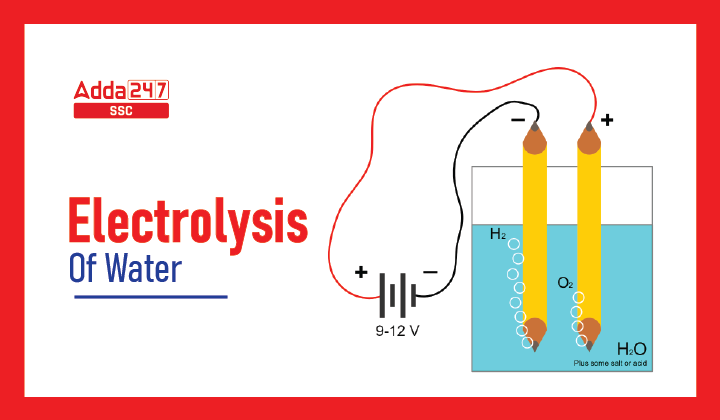
Materials required: Beaker, Rubber stopper, Carbon electrodes (anode & cathode), Battery, Water, Dilute sulfuric acid and Test tube.
- Insert the anode and cathode carbon electrodes into the Beaker using rubber stoppers at the lid.
- Connect a 6-volt battery to these carbon electrodes.
- Fill the beaker halfway with water so that the carbon electrodes are submerged.
- To this water, add a few drops of sulfuric acid.
- Fill two test tubes with water, then invert the test tubes onto the carbon electrodes.
- Turn on the current from the 6-volt battery.
- Allow the apparatus to rest for a while.
Results:
There will be bubble formation at both electrodes in the test tubes (which means gas is forming or liberating from water). Water begins to move in the test tube as a result of the formation of bubbles. followed by collection of Gases in both test tubes. The Gas collected at the Anode is Oxygen, and the Gas collected at the Cathode is Hydrogen.
Confirmatory Test:
- Carefully remove the test tubes from the mug once they have been filled with the gases.
- To Confirm presence of Hydrogen: Place a lit candle near the mouth of one of the test tubes, the gas ignites and burns with a pop sound, indicating the presence of hydrogen in the test tube.
- To Confirm presence of Oxygen: When we place a burning candle near the mouth of another test tube, the candle begins to burn brightly, indicating that the test tube contains oxygen.
Electrolysis of Water Diagram
The schematic diagram representing electrolysis of Water is provided here. It is suggested to understand the concept of Electrolysis by using the diagram and relating to the step by step procedure. The electrolysis of water diagram is given below:
Reaction involved in Electrolysis of Water
The Chemical Reaction for the Electrolysis of Water involves Redox Reaction. The electrolysis of water reaction produces hydrogen and oxygen gases. The Electrolytic Cell is made up of a pair of Electrodes immersed in water with a small amount of an Electrolyte such as H₂SO₄ used above. The electrolyte is required because pure water cannot carry enough charge due to a lack of ions. The schematic representation of the Reactions involved in the process of Electrolysis is given below:
Overall Reaction
2H2O(l) → 2H2(g) + O2(g)
At Anode:
2H2O(l) → O2(g) + 4H+(aq) + 4e−
At Cathode:
2H2O(l) + 2e− → H2(g) + 2OH−(aq)
Applications of Electrolysis of Water
The electrolysis of water has several important applications across various industries. Here are the key applications:
1. Hydrogen Production:
- Clean Energy Source: Hydrogen gas produced via water electrolysis is a clean fuel that can power hydrogen fuel cells, vehicles, and industrial processes.
- Renewable Energy Storage: Excess energy from renewable sources (like wind or solar) can be stored as hydrogen gas, which can later be used to generate electricity.
2. Oxygen Production:
- Medical Use: The oxygen generated during electrolysis can be used in medical applications, such as supplying oxygen to hospitals.
- Industrial Use: Oxygen is used in welding, metal cutting, and various chemical manufacturing processes.
3. Space Exploration:
- Life Support Systems: Electrolysis is used on spacecraft to produce breathable oxygen for astronauts.
- Rocket Fuel Production: The hydrogen and oxygen produced can be used as rocket propellants.
4. Energy Sector:
- Green Hydrogen Economy: Electrolysis is central to producing green hydrogen, a key element of decarbonizing industries like transportation, steel, and ammonia production.
- Fuel Cells: The hydrogen produced can be used in fuel cells for generating electricity in a clean and efficient way.
5. Water Treatment and Desalination:
- Electrolysis can aid in purifying water by breaking down contaminants.
- It can be integrated with renewable energy systems for off-grid water treatment solutions.
6. Industrial Chemical Production:
- Hydrogen and oxygen generated are raw materials for producing chemicals like ammonia via the Haber process or hydrogen peroxide.
7. Laboratory and Educational Use:
- Electrolysis of water is a common experiment to demonstrate the principles of electrochemistry and the composition of water.
8. Environmental Applications:
- Carbon Sequestration: Hydrogen produced via electrolysis can be combined with captured Carbon dioxide to produce synthetic fuels, reducing carbon emissions.
- Pollution Control: Oxygen can be used in wastewater treatment plants for aeration and improving the breakdown of pollutants.
These applications highlight the significance of water electrolysis in advancing sustainable and innovative technologies.
Frequently Asked Question
Q1. Which electrodes are used in the electrolysis of water?
Ans. Platinum electrodes are used in the electrolysis of water.
Q2. Which type of chemical reaction is the electrolysis of water?
Ans. Electrolysis of water is a decomposition reaction as water splits into its constituent elements, hydrogen, and oxygen, under the effect of an electric current.
Q3. What happens during the electrolysis of water?
Ans. During the electrolysis of water, water decomposes into oxygen gas and hydrogen gas. An electric current is passed through the solution to accomplish this. The cathode generates hydrogen gas, while the anode generates oxygen gas.


 Delhi Sultanate, Notes on Dynasties of M...
Delhi Sultanate, Notes on Dynasties of M...
 Free Study Material for SSC CGL 2025, Do...
Free Study Material for SSC CGL 2025, Do...
 Free Study Material for CBSE Junior Assi...
Free Study Material for CBSE Junior Assi...


