Table of Contents
Weather and Climate
Weather and climate play crucial roles in shaping our daily lives and the overall state of our planet. While often used interchangeably, weather and climate are distinct yet interconnected concepts that involve the study of atmospheric conditions and long-term patterns. By understanding the dynamics of weather and climate, we can gain insights into the fluctuations we experience in our local environments and recognize the broader implications for the Earth as a whole. In this article, we will dig into the fundamental differences and similarities between weather and climate.
Weather and Climate Definition
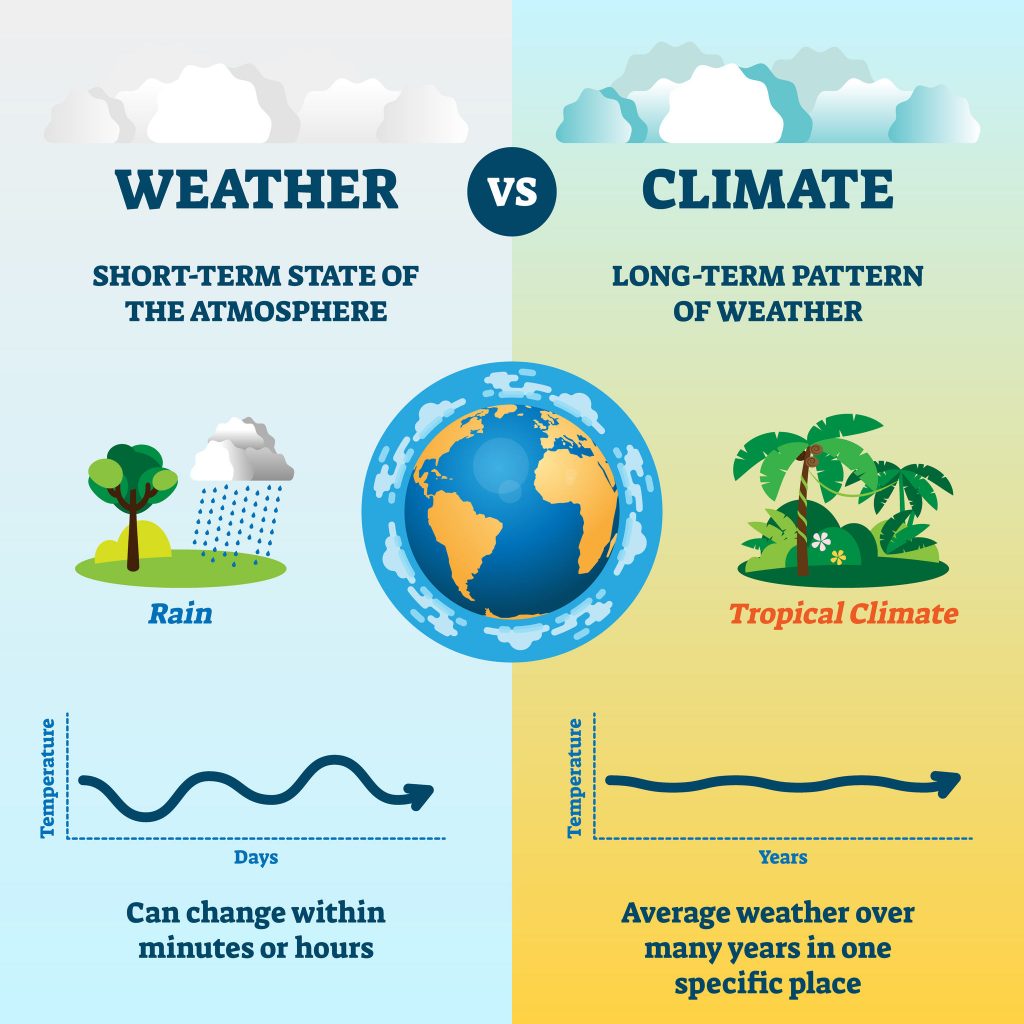
Weather is basically the way the atmosphere is behaving, mainly with respect to its effects on life and human activities. The difference between weather and climate is that weather consists of short-term (minutes to months) changes in the atmosphere. It can change from minute-to-minute, hour-to-hour, day-to-day, and season-to-season.
Climate describes the long-term weather patterns in a specific area. Scientists define climate as the average weather for a specific region and period, usually over a 30-year period. It’s an average weather pattern for a specific region. When scientists talk about climate, they’re looking at averages of precipitation, temperature, humidity, sunshine, wind velocity, phenomena such as fog, frost, and hail storms, and other measures of the weather that occur over a long period in a particular place.

Difference between Weather and Climate
Some differences between weather and climate are given below:
|
Sr. No. |
Weather |
Climate |
|
1. |
The day-to-day information of atmospheric changes in a particular area at a specific time is called weather. |
Climate is the statistical information of the average weather condition of a specific region for more than 30 years. |
|
2. |
The weather of a place includes the short-term atmospheric condition. Also, these atmospheric conditions can change within a short period like minutes, hours, days, etc. |
The climate of a country or zone includes the long-term average atmospheric conditions. Thus, the climate is the average weather information observed over decades. |
|
3. |
The atmospheric elements of weather are air pressure, humidity, wind, temperature, rain, cloudiness, storms, snow, precipitation, etc. These conditions can affect the weather of the place within a short time. |
When the atmospheric elements of weather are observed over the decades, those become the affecting conditions of climate. These conditions can include temperature, humidity, wind, etc. |
|
4. |
The weather of a particular location can have an impact on daily human activities such as occupation, transportation, communication, agriculture, and so on. |
The climate of a country has a significant impact on industries, agriculture, and the livelihood of the people who live there. |
|
5. |
Weather conditions change very frequently. |
Climate conditions change over a long period. |
|
6. |
The meteorological department of a place observes the changes in weather conditions. Meteorology is the study of weather forecasting. |
Institutes of climate studies observe and predict the changes in climate. This study is called climatology. |
Weather and Climate Similarities
Weather and Climate similarities go as follows:
- Both weather and climate are the states of atmospheric conditions of a place.
- Weather and climate include atmospheric characteristics such as precipitation, temperature, humidity, wind, pressure, etc.
- They do not always occur in the same pattern everywhere, hence they vary across the world.
- Both weather and climate are atmospheric sciences.
The Elements of Weather and Climate
The various elements of weather and climate are temperature, atmospheric pressure, wind, humidity, precipitation, cloudiness, visibility, duration of sunshine, etc.
Temperature
- Temperature is a measurement of the amount of kinetic energy in the air that occurs physically as heat or cold.
- A thermometer is a device that measures temperature.
Atmospheric Pressure
- It’s also one of the most important factors in precise weather forecasting.
- The pressure formed by the weight of air in the Earth’s atmosphere is known as air pressure.
- It’s also known as barometric pressure, named after the device that measures air pressure.
- Due to the gravitational force of the Earth, the weight of the particles in the air causes pressure.
Wind
- The wind is responsible for extreme weather occurrences such as cold and warm fronts, clouds, thunderstorms, and hurricanes.
- The wind is the large-scale movement of air in the atmosphere from a high-pressure location to a low-pressure area.
- The distance between low and high-pressure areas, as well as the difference in air pressure, define wind speed and strength.
- The anemometer is a device that measures wind speed. A wind vane (also known as a weather vane) is a device that is used to determine the direction of the wind.
Precipitation
- Precipitation is water in all of its forms, which is generated when water vapour condenses into a solid form and falls to the earth when it gets too heavy to remain suspended in the air.
- Rain, snow and hail are all examples of precipitation.
- Evaporation and condensation are the primary causes of precipitation.
- A rain gauge is a device that measures rainfall.
Humidity
- Humidity refers to the amount of water vapour in the atmosphere at any given time.
- Water vapour is simply water that has turned into a gas (after the liquid has evaporated).
- The hygrometer is a device that measures wind speed
Visibility
- The degree to which an object can be observed over a given distance is measured as visibility.
- It is useful in environments where visibility is critical, such as airports and harbours.
- The tools used to detect visibility include visibility sensors such as the “forward scatter sensor.”
Clouds
- Clouds are water droplets or water in various states (such as ice and snow crystals) that form when water vapour reaches a point where it can no longer continue in a gaseous state.
- Modern devices used to analyze clouds are weather satellites and radars.
Duration of Sunshine
- The length of time the Earth’s surface is directly exposed to solar radiation is known as sunshine duration. It is also known as sunshine hours.
- Solar duration has an impact on other meteorological elements, which can alter the overall makeup of the weather.
- Campbell–Stokes recorders are instruments that are used to record the length of time that the sun is visible.
| Check Related posts: | |
| State and Capitals in India | 8 Union Territories in India |
| Dams In India | Largest State of India |



 National Animal of India: Royal Bengal T...
National Animal of India: Royal Bengal T...
 Government Jobs After 10th, Government J...
Government Jobs After 10th, Government J...
 RRB Group D Applicants Data 2025 Release...
RRB Group D Applicants Data 2025 Release...


